Community Information
A Voter’s Dictionary of Important Terms
The average voter probably never imagined needing to know every term in the vocabulary of politics. But in order to fully participate in your civic duty, you may want to know what the newscasters are talking about when they use this jargon. The following are 30 commonly used words and phrases that pertain to the election process. Read it all through, refer back to it as needed, and share it with others, because a strong democracy is powered by an informed population.
Once you've had a chance to brush up on these voting terms, Join Grand Central Library, along with the League of Women Voters NYC for a free online civics trivia extravaganza on February 24th.
Absentee Ballot - traditionally used by citizens who will not be able to get to their polling site during early voting and election day. Examples include active military personnel, persons in jail, persons with disabilities, persons in the hospital, those living abroad or going to school in a different area, and more. During the 2020 elections, accommodations were made in many states due to the risk of contracting COVID-19 at the polling sites.
Ballot - the physical item on which votes are cast—typically in writing and in secret before submitted for counting.
Blue State - refers to a U.S. state where the majority of voters usually support Democratic candidates and causes.
Canvassing - the process of contacting voters to ask for support for a certain candidate or policy. Typically coordinated by the candidate’s team and often involves volunteer supporters.
Caucus - a meeting of registered members of a particular political party meet to discuss issues, policies, and, generally, express support for candidates.
Constituent - a voting member of a community or organization and having the power to appoint or elect.
Convention - an event where chosen or elected officials from each party announce which candidate they are supporting for an upcoming election.
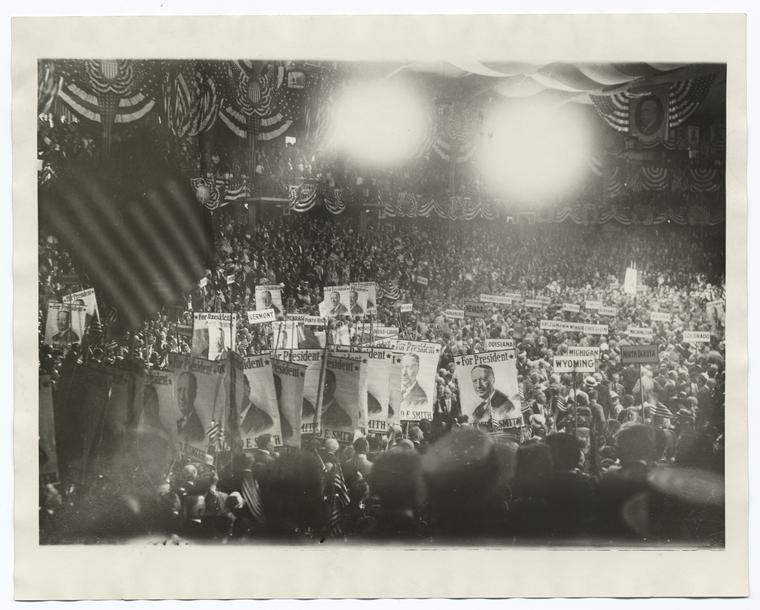

Department of Elections - an administrative body that oversees election proceedings and voting activity. The department is a bipartisan board appointed by local officials; in New York City the Board of Elections is composed of ten Commissioners, two from each borough upon recommendation by both political parties and then appointed by the City Council for a term of four years.
District - a geographical area with distinct representation in the Senate and Congress. Each house is part of a Senatorial and Congressional District. (These can change over time)
Early Voting - the opportunity to cast your ballot in person earlier than election day. Early voting policies vary by state. In New York State, the Board of Elections is required to provide nine additional days to cast a ballot in person prior to Election Day. (https://www.voteearlyny.org/about-early-voting/)
Electoral College - composed of electors chosen by the political parties of each state. Each state has its own system for appointing electors. They pledge to vote for the candidate who received the most popular votes in their state.
There are 538 Electoral votes, which corresponds to each state's Congressional delegation. There are 435 elected Representatives in Congress from each of the 50 states, three electors from the District of Columbia (They are not represented in Congress) and 100 senators in the US Senate. 435+3+100 = 538 Electors. 270 electors are needed to elect the President of the United States. Citizens in Puerto Rico, Guam, and US Virgin Islands have no electors.
Electoral College Map - a map which uses colors to represent the political party of the winning candidate in each state. Red is for Republicans and Blue is for Democrats. The physical size of each state is not related to the number of votes or population of the state. For example, MT appears very large on the Electoral Map but its population is very low and it only has 3 electoral votes. ME and NE divide up their electoral votes proportionally instead of awarding “winner takes all.” You can win the popular vote yet lose the election. The total nationwide popular votes for the losing candidate can be greater than for the winning candidate because electoral votes are “winner takes all.” States with large populations may have several million votes supporting the losing candidate compared with much smaller total votes cast in less populated states for winning candidates.
Exit Polls - survey data of voters leaving a polling place after they have voted. Researchers pull from a sample of these voters—often voters who voluntarily speak with researchers outside the polling place—to assess how their votes were cast to get a picture of the election outcome.
Faithless electors - electors of the electoral college who don't cast their vote in correspondence with the popular vote in their state. This happens rarely and has yet to swing a presidential election.
Incumbent - an individual currently holding an elected position.
Landslide - a victory that is won by a large majority, rather than just by a few points.
Participatory Budgeting - a democratic process available in some places in which community members directly decide how to spend part of a public budget. http://ideas.pbnyc.org/page/about
Platform - a political party’s or candidate’s position on certain issues. It is usually a written statement of principles and goals.
Polling Site - the place you go to cast your ballot. You are assigned a polling site based on your home address and can only cast a ballot at that site.
Popular vote - the total number of votes cast by registered voters including in-person and absentee/mail-in.
Ranked-Choice Voting (RCV) - an electoral system in which voters rank candidates by preference on their ballots. If a candidate wins a majority of first-preference votes, he or she is declared the winner. If no candidate wins a majority of first-preference votes, the candidate with the fewest first-preference votes is eliminated. http://www.nyccfb.info/nyc-votes/ranked-choice-voting/
Red State - refers to a U.S. state where the majority of voters usually support Republican candidates and causes.
Redistricting - the process of redrawing geographic boundaries that represent congressional districts.
Referendum - also called a proposition or ballot initiative, is another portion of the ballot that asks you to vote on a piece of legislation.
Split-Ticket Voting - voting for candidates of different parties for various offices in the same election. For example, voting for a Republican for Senator and a Democrat for President.
Straight-Ticket Voting - voting candidates who are all of the same party. For example, voting for Republican candidates for Senator, Representative, and President.
Super Tuesday - during Presidential primary season it is a day on which a large number of states hold their elections so the results of that day could make or break a candidate.
Swing State - a state that is closely split between Republican and Democratic voters. In Presidential elections, the electoral votes of swing states are significant in determining the outcome.
Term Limit - the amount of time that an elected official retains their office. Different offices have different term limits and a new election takes place at the end of the term.
"Winner takes all” - all the electoral votes from a state are awarded to the candidate who wins the popular vote in that state.
LEARN MORE
- Doubletalk: The Language, Code, and Jargon of a Presidential Election by Chuck McCutcheon
- Credo Reference Database: Provides full-text online access to hundreds of multidisciplinary reference book collections, bilingual dictionaries, and encyclopedias.
- U.S. History in Context Database: Coverage of the most-studied U.S. history topics, with overview articles, primary sources, biographies, audio, images, news and magazine articles, academic journals, and legal case overviews.
IMPORTANT 2021 VOTING DATES for NYC:
- June 22nd is the primary for New York City Mayor
- November 2nd is the general election for New York City Mayor
Inspiration for this blog post and references for definitions come from the following:
Read E-Books with SimplyE
 With your library card, it's easier than ever to choose from more than 300,000 e-books on SimplyE, The New York Public Library's free e-reader app. Gain access to digital resources for all ages, including e-books, audiobooks, databases, and more.
With your library card, it's easier than ever to choose from more than 300,000 e-books on SimplyE, The New York Public Library's free e-reader app. Gain access to digital resources for all ages, including e-books, audiobooks, databases, and more.
If you don’t have an NYPL library card, New York State residents can apply for a digital card online or through SimplyE (available on the App Store or Google Play).
Need more help? Read our guide to using SimplyE.
Comments
Very informative, thanks!
Submitted by Melissa S (not verified) on March 1, 2021 - 6:19pm